Setup - Asset Type
Integrate your external assets into Jira, making them easily searchable and linkable through a dedicated custom field. In this guide, we will walk you through the setup of a search field for the External Data for Jira Extension App.
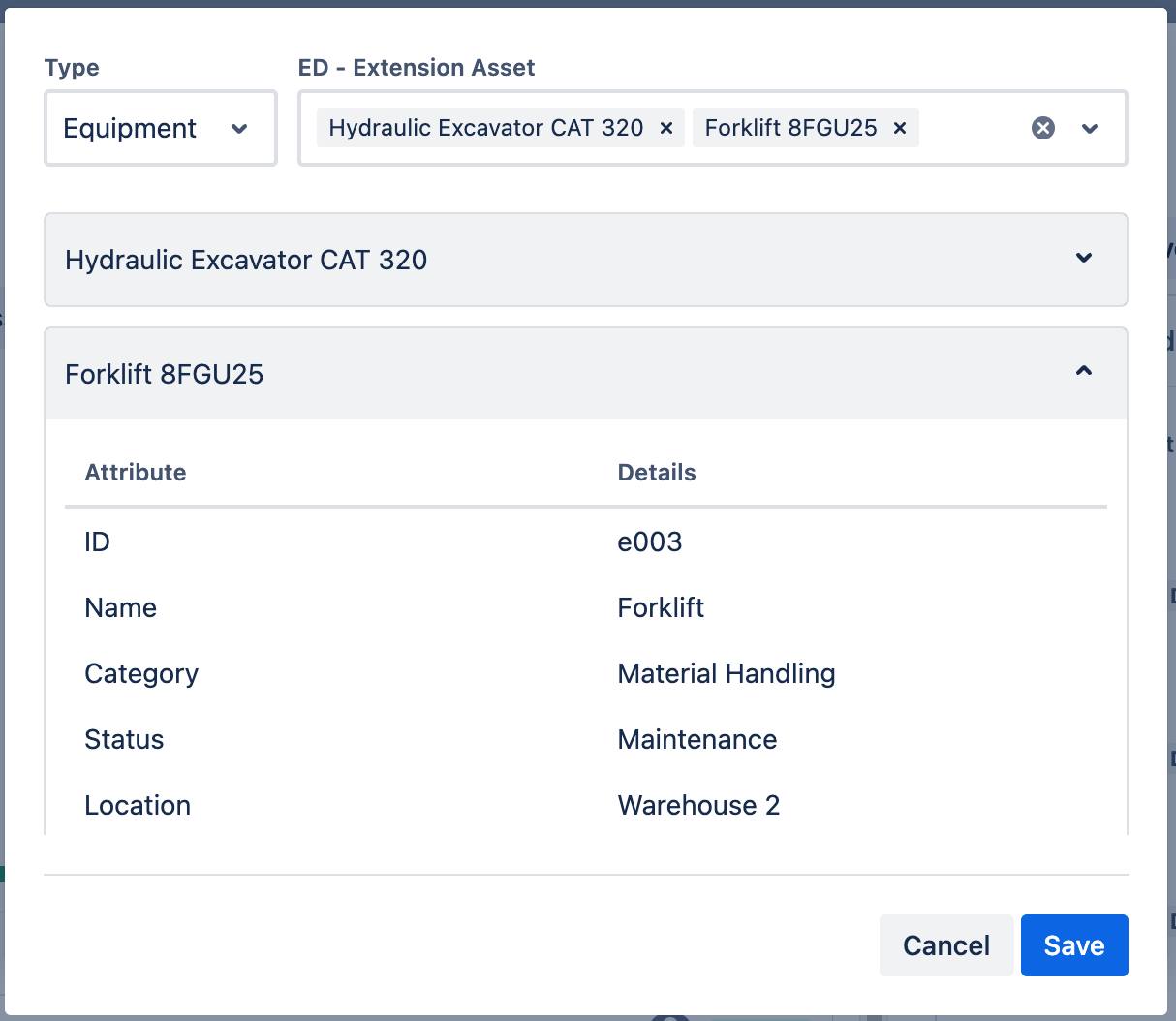
Example of an Extension Asset Field
Prerequisites
Please ensure that the External Data for Jira Extension is both installed and connected to your main app.
How it Works
During setup, a separate field must be configured for each asset type, suitably called Asset Type.
It is possible to link multiple asset types to the same custom Extension Asset Field. To create multiple asset types, you need to add another field configuration 'Extension Asset Type'. This configuration enables the inclusion of multiple asset types within the same target Jira Field.
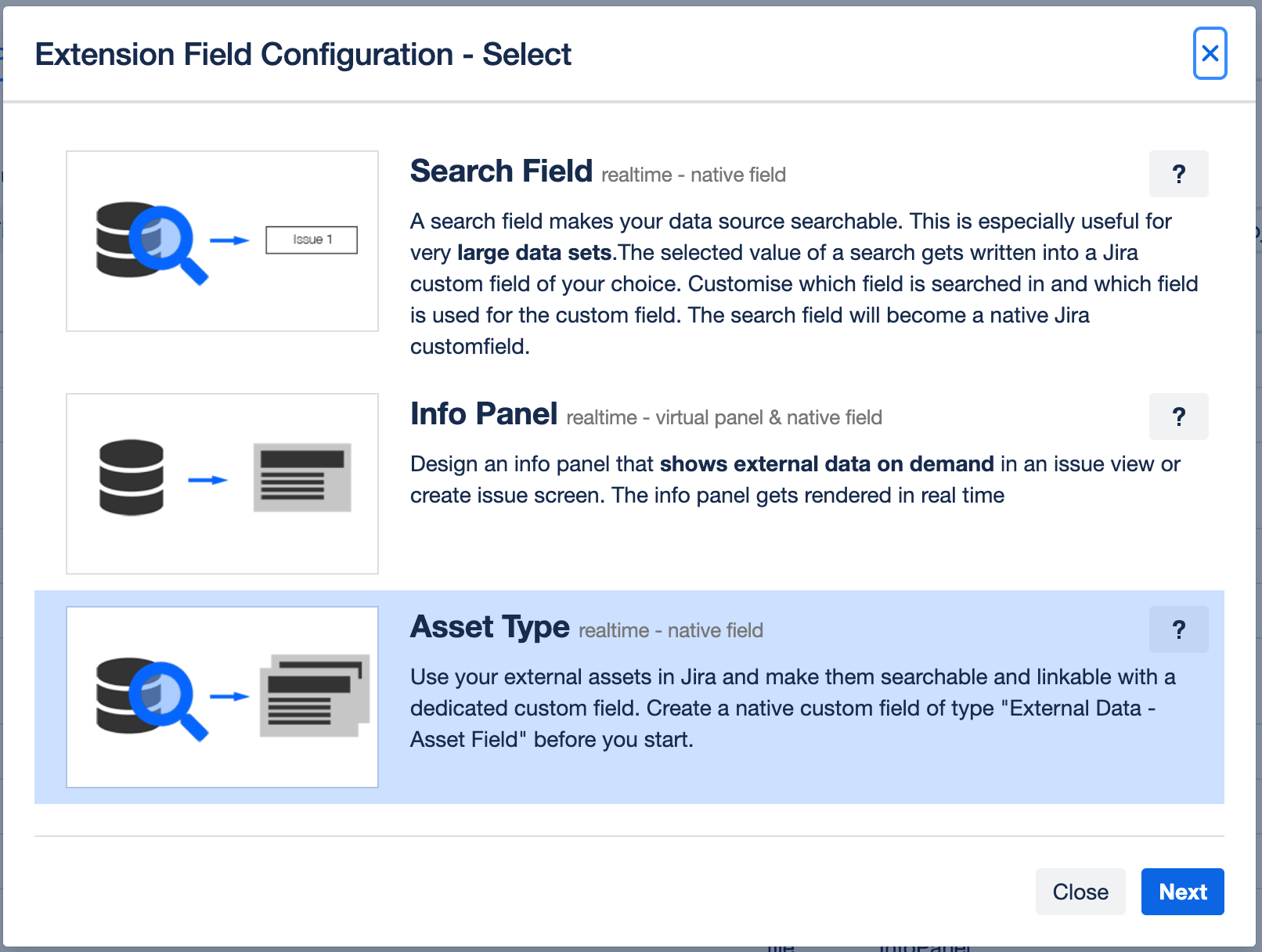
For an optimal configuration of each asset type, three key components must be defined:
Data Source: Specifies the source from which the assets are obtained.
Selection Method: Defines the method for selecting assets from the data source.
Detail Template: Determines a layout that defines how the detailed information for each selected asset will be displayed.
Creating a New Custom Field
First, we need to create a new custom field. Navigate to Available Jira Fields in the main app and select + Add Custom Field. When the "Create new custom field" modal appears, choose External Data - Asset Field as the field type. Alternatively, this field can also be set up via the Jira settings.
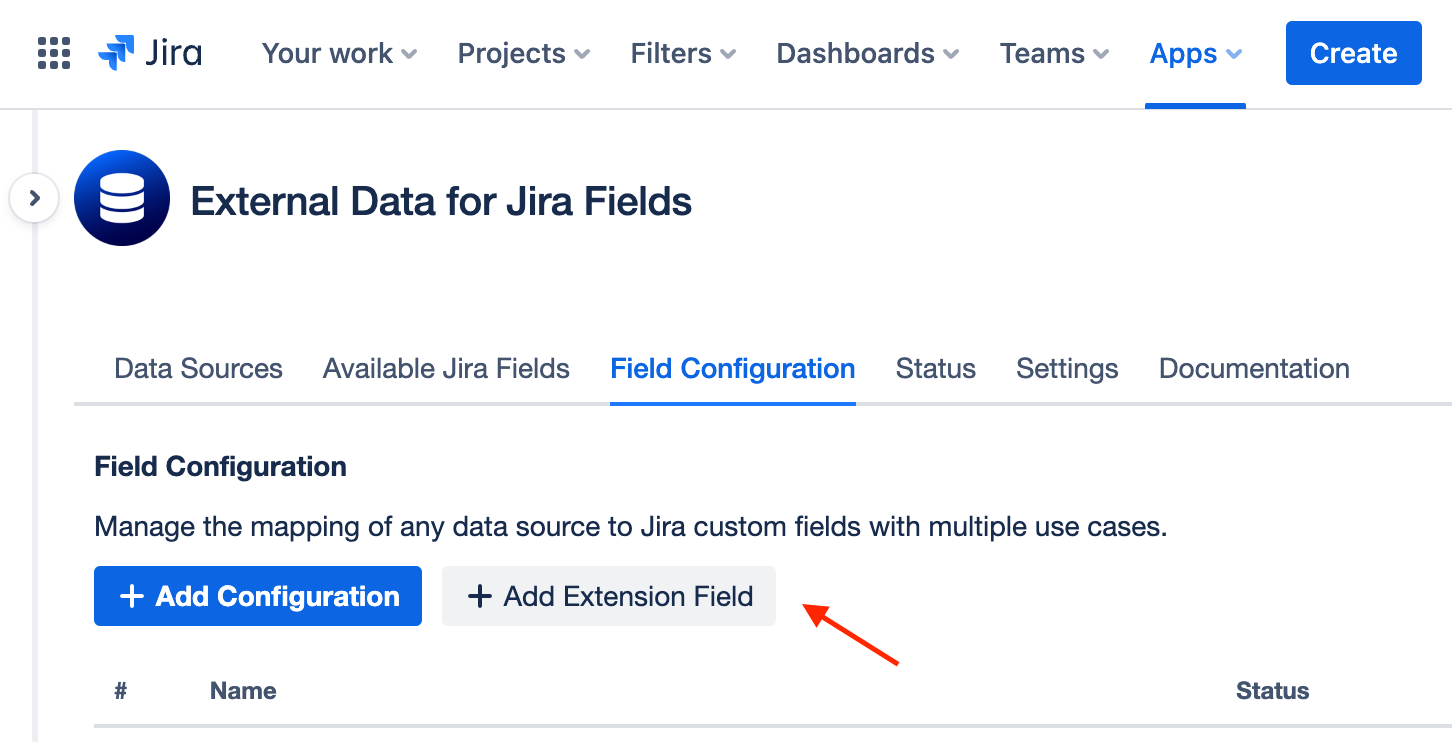
Create a New Field Configuration for Each Asset Type
Navigate to Field Configuration > Add ExtensionField
Select the relevant configuration type.
Data Source
After you have selected a data source, the unprocessed results of your selection are displayed below the input field.
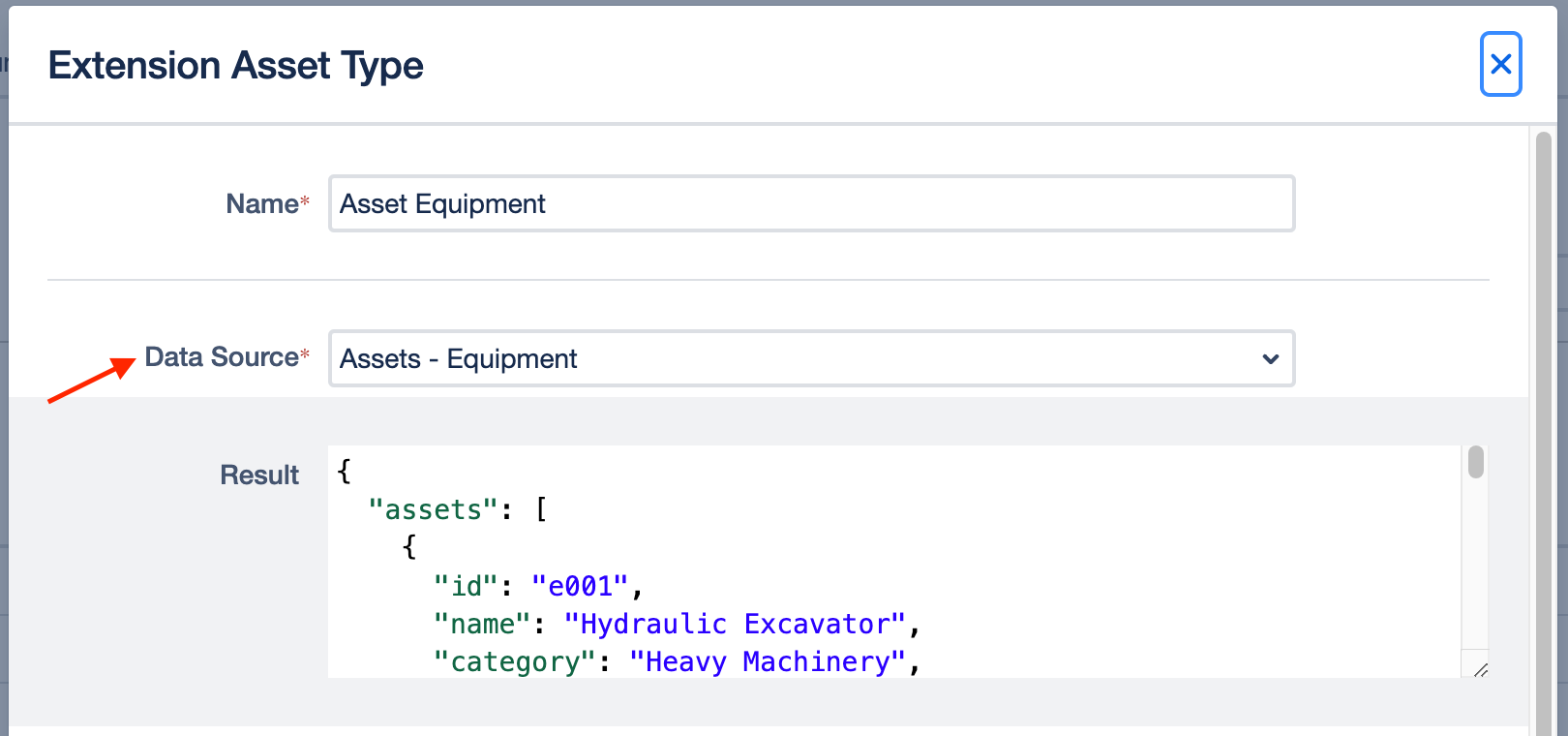
Example:
{
"assets": [
{
"id": "e001",
"name": "Hydraulic Excavator",
"category": "Heavy Machinery",
"status": "Available",
"location": "Warehouse 1",
"manufacturer": "Caterpillar",
"model": "CAT 320",
"year": 2018,
"lastMaintenanceDate": "2023-03-15"
},
{
"id": "e002",
"name": "Electric Generator",
"category": "Power Supply",
"status": "In Use",
"location": "Site 4",
"manufacturer": "Honda",
"model": "EU2200i",
"year": 2020,
"lastMaintenanceDate": "2023-02-20"
}
]
}Target Jira Field
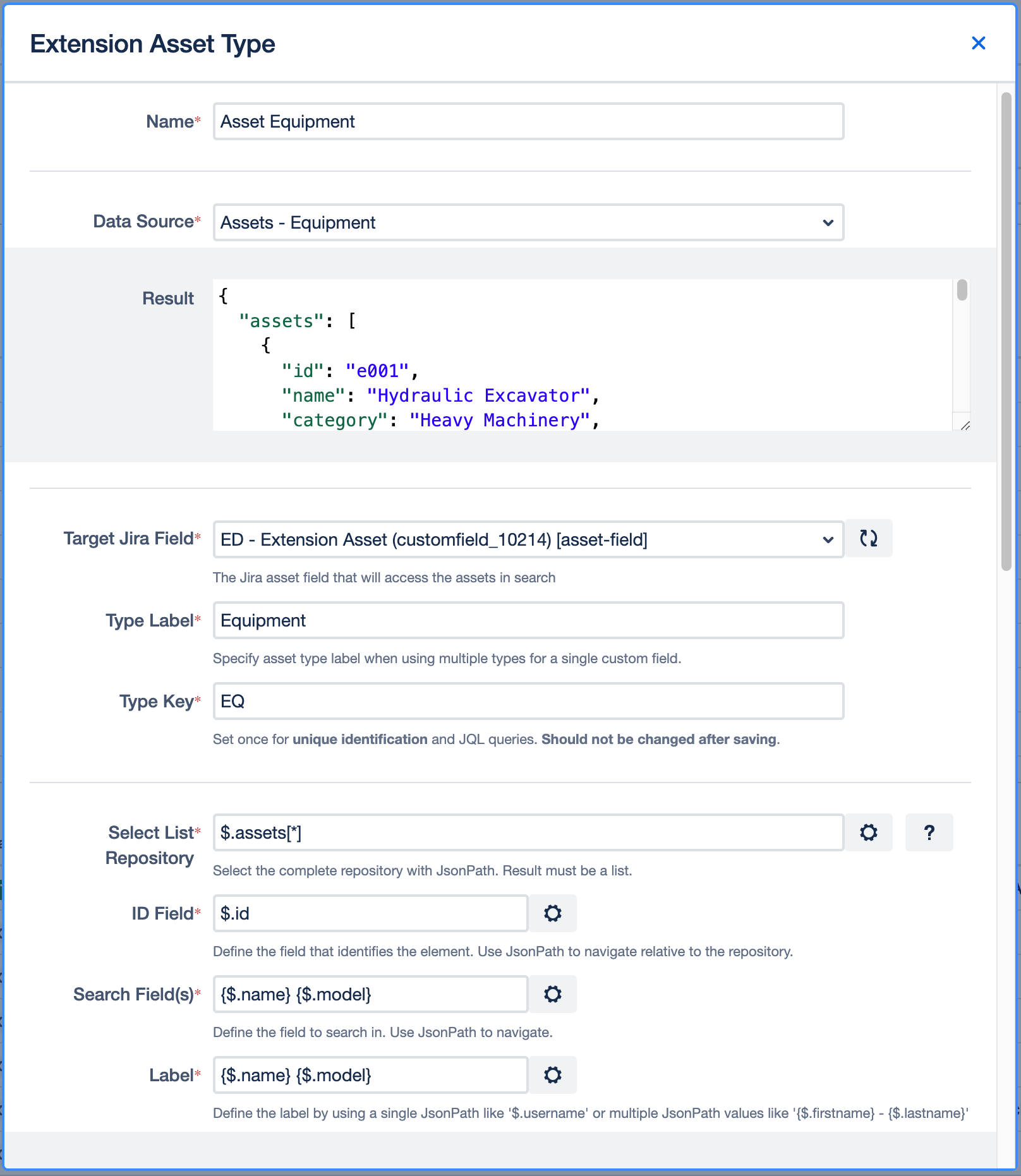
The Target Jira Field specifies the custom field in Jira to which the configuration will be assigned.
Type Label
Assign a Label to the Asset Type
Example:
EquipmentType Key
Establish a key for unique identification and JQL queries.
Example:
EQSelect List Repository
Add the JSON path including the name of your data list here. Please make sure to not just select a single value.
Example:
$.assets[*]ID Field
ID is the unique identifier that identifies an item within your data set (must be a unique number or string).
This field is used to identify a selected value later. You can use the same JSON path in the value field and the search field.
Example:
$.idSearch Field
Define the underlying field value(s) (again, as JSON path) that you want to use as basis for the search. Field values should always refer to the values in your data source.
(When a user starts typing in the search field, only the respective value(s) will be displayed as matches)
Example:
$.nameor
{$.name} {$.model}Using multiple fields like this will let you search in name & model.
Label Field
Define JSON path(s) to the values in your data source that are supposed to be displayed as selected values.
Example:
$.nameor
{$.name} {$.model}The configuration for our example should now look like this:
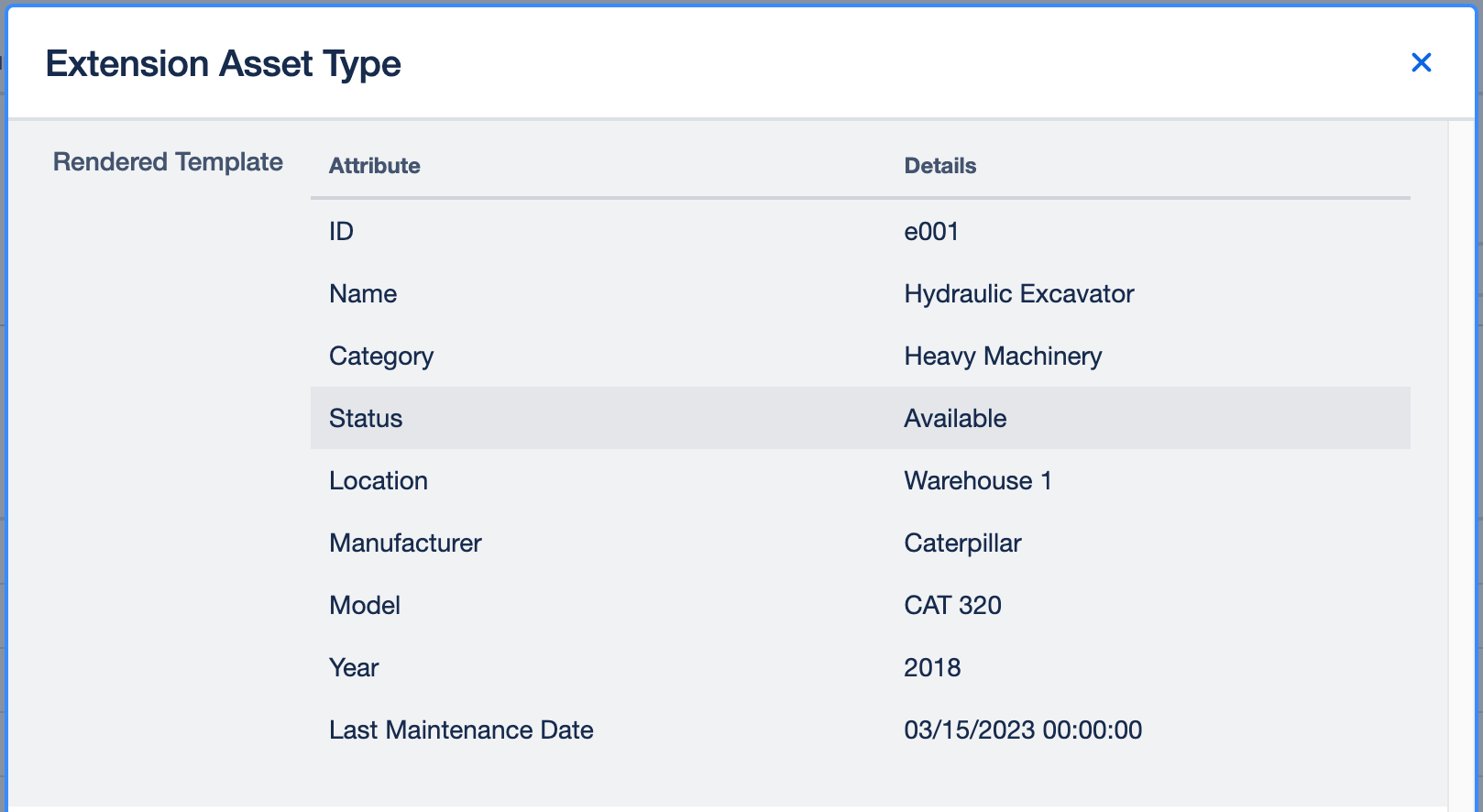
Detail Template
Here you can use HTML to display the result the way you want with maximal flexibility. The selected asset can be used with the mustache syntax. All CSS classes from AUI can be used inside the template to fit well into JIRA.
To show all values from the example we use the following template:
<table class="aui aui-table-list">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Attribute</th>
<th>Details</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>ID</td>
<td>{{ id }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Name</td>
<td>{{ name }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Category</td>
<td>{{ category }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Status</td>
<td>{{ status }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Location</td>
<td>{{ location }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Manufacturer</td>
<td>{{ manufacturer }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Model</td>
<td>{{ model }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Year</td>
<td>{{ year }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Last Maintenance Date</td>
<td>{{ lastMaintenanceDate }}</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
See the Template Syntax section for more details on creating more complex templates and the Advanced Tables section for creating rich tables.
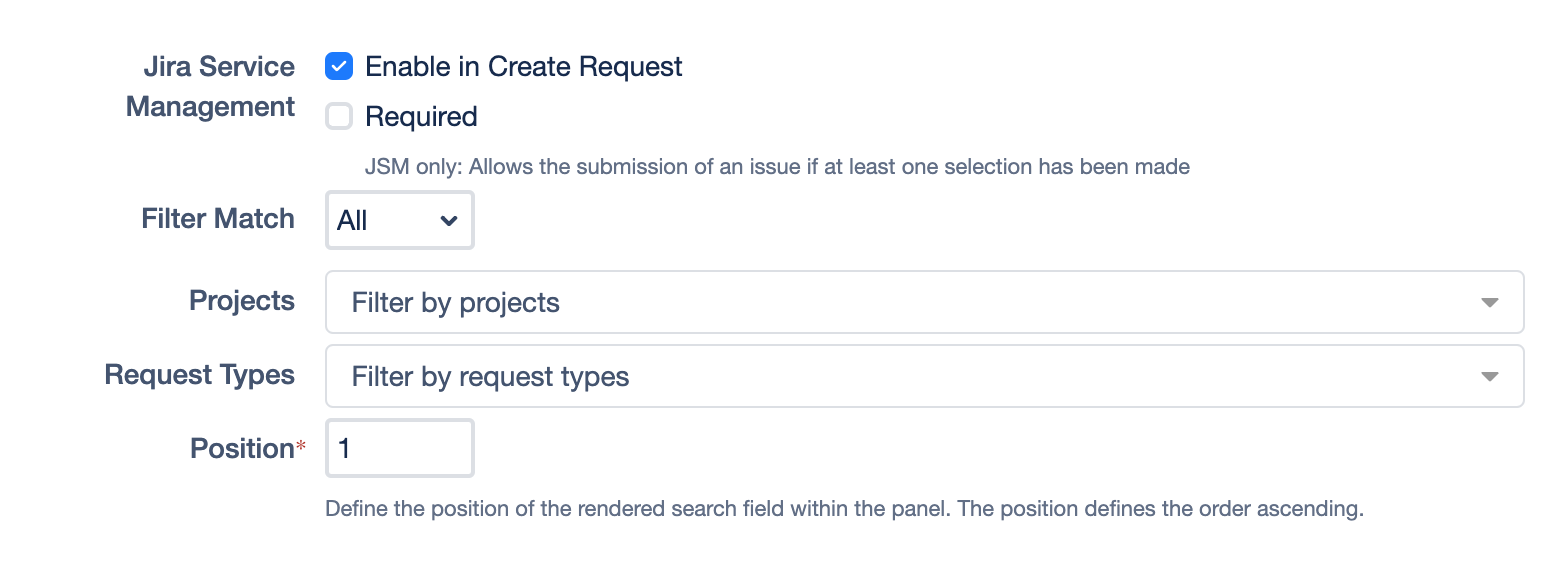
Enable in JSM Create Request
This option activates the asset field on the screen for creating a request in the Jira Service Management customer portal. You can also set these fields as required and/or read-only fields..
Filter Match (Optional)
You can filter the search to only match specific spaces, work types or request types. By selecting Any, you’ll get results that matches any of the selected filters while choosing All means, all of the defined filters must apply for matches in order to be shown.